바위타는 두루미
[leetcode]160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists 본문
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
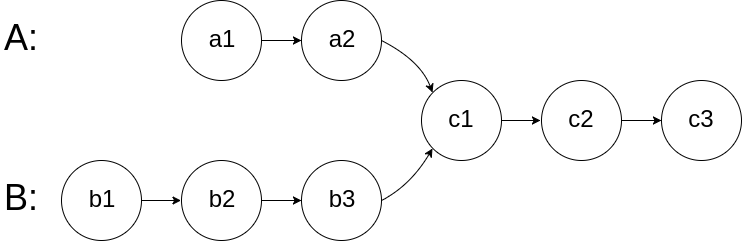
begin to intersect at node c1.
Example 1:
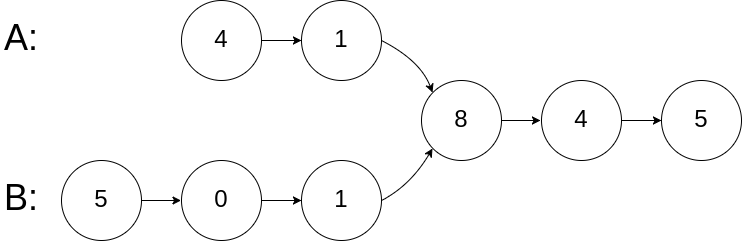
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 Output: Reference of the node with value = 8 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
Example 2:

Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 Output: Reference of the node with value = 2 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
Example 3:

Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 Output: null Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values. Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
- The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
나의 solution :
우선 한번 순회를 통해 A, B의 길이와 각 끝점이 만나는지를 확인한다.
만나지 않으면 둘의 intersection은 없기 때문에 None을 반환한다.
그리고 길이가 긴쪽의 포인터를 차이만큼 움직여서 같은 길이에서 탐색을 시작해서 같은 점을 발견하면 그점이 intersection!
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def changeStart(self,head, cnt):
while cnt >0:
head = head.next
cnt -=1
return head
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
tailA, tailB = headA, headB
cntA, cntB = 0, 0
while tailA :
tailA = tailA.next
cntA +=1
while tailB :
tailB = tailB.next
cntB +=1
if tailA != tailB :
return None
if cntA > cntB :
headA = self.changeStart(headA, cntA-cntB)
elif cntB > cntA :
headB = self.changeStart(headB, cntB-cntA)
while headA != headB:
headA = headA.next
headB = headB.next
return headA
신기한 솔루션
class Solution(object):
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
a, b = headA, headB
while a != b:
if a is None:
a = headB
else:
a = a.next
if b is None:
b = headA
else:
b = b.next
return a
'Study > Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [leetcode]103. Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal (0) | 2019.08.09 |
|---|---|
| [leetcode]94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal (0) | 2019.08.09 |
| [leetcode] 2. add two numbers (0) | 2019.08.07 |
| [프로그래머스]도둑질 (3) | 2019.08.01 |
| [프로그래머스]단어변환 (0) | 2019.08.01 |

